Gross Anatomy and Functions of Skeletal Muscles
Muscles of the Vertebral Column



Muscle Nomenclature
Functional Groups
1) Prime mover – provides major force of movement.
2) Antagonist – oppose or reverse a particular movement; is often stretched when prime mover is active; help regulates action of prime mover by contracting somewhat to provide resistance that prevents overshoot or slows movement.
3) Synergists – help prime mover muscles by adding extra force to same movement or by
reducing undesirable or unnecessary movements that might occur during the action of a
prime mover; if they immobilize a bone or a muscle’s origin, they are called fixators.
Muscle Names
a. Location – usually muscle name indicates body or body region with which muscle is
associated; can indicate position relative to other similarly named muscles.
• e.g., major, minor, external, internal
b. Shape – some muscles are named for their distinctive shape.
• e.g., triangular (=deltoid), trapezoidal (=trapezius)
c. Size – name indicates large, internediate, or small size.
• e.g., largest (=maximus), smallest (=minimus), intermedius, longest (=longus), shortest (=brevis)
 |
| Muscle Attachment |
d. Fiber Direction – name indicates direction of fibers either in reference to imaginary line or in reference to body position.
• e.g., straight (=rectus), right angles/oblique (=transversus or oblique)
e. Number of Origins – if muscle has multiple origins, the name can indicate how many.
• e.g., biceps = 2 origins, triceps = 3 origins, quadriceps = 4 origins
f. Origin and Insertion – name indicates origin and insertion points; origin name always comes first.
• e.g., sternocleidomastoid – inserts on mastoid, originates on sternum and clavicle.
g. Action – can be named for the action they do.
• e.g., flexor, extensor, adductor, supinator
h. Multiple Criteria – can be named using combinations of above schemes.
• e.g., extensor carpi radialis longus
• muscle action = extension
• joint it acts on = carpus/wrist
• position = close to radius
• size = long
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles – operation is based on use of leverage
a. bones are levers – allows movement of heavy load or faster movement of load
• 1st class levers: effort applied at one end of lever, load at other end, fulcrum in between.
(e.g., gastrocnemius, triceps)
• 2nd class levers: effort applied at one end of lever, fulcrum at other end, load in between
(e.g., wheelbarrow, gastrocnemius if you use it to stand on toes)
• 3rd class levers: effort is applied between load and fulcrum
(e.g., biceps, deltoids, hamstrings, etc.)
• power levers have mechanical advantage
• load is close to fulcrum and small effort is applied far from fulcrum (e.g., car jack,
adductor muscles)
• speed levers have mechanical disadvantage
• load is far from fulcrum and effort is applied near fulcrum; effort exerted must be
greater than load moved or supported (e.g., gluteal muscles)
b. joints are fulcrums
c. muscles and their contraction are the applied force or effort
Muscle Anatomy
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Overview of the Superficial Body Musculature FACIAL MUSCLES 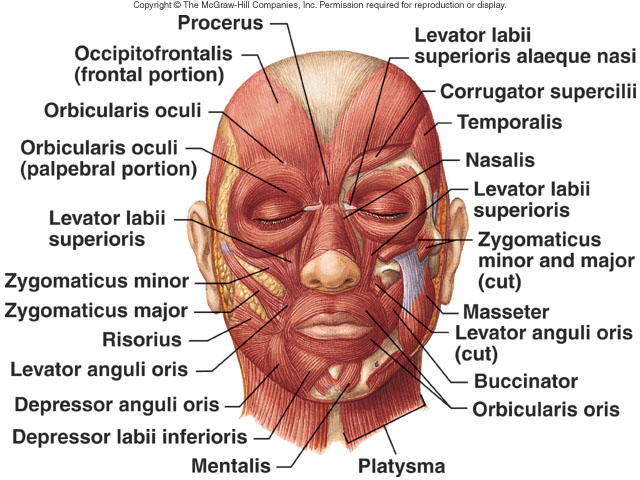 Anterior View  Lateral View Muscles of Facial Expression
|
Muscles of Mastication

Hyoid Muscles
Suprahyoid Muscles
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | |
| digastric | anterior belly - digastric fossa (mandible); posterior belly - mastoid process of temporal bone | Intermediate tendon (hyoid bone) | anterior belly - mandibular division of the trigeminal(CN V) via the mylohyoid nerve; posterior belly -facial nerve (CN VII) | Opens the jaw when the masseter and the temporalis are relaxed. | ||
| stylohyoid | styloid process (temporal) | greater cornuof hyoid bone | facial nerve (CN VII) | Elevate the hyoid during swallowing | ||
| mylohyoid | Mylohyoid line (mandible) | Median raphé | mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery | mylohyoid nerve, from inferior alveolar branch of mandibular nerve [V3] | Raises oral cavity floor,elevates hyoid, depresses mandible | |
| geniohyoid | Symphysis menti | hyoid bone | C1 via hypoglossal nerve | carry hyoid bone and the tongue upward during deglutition |
Infrahyoid Muscles
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Artery | Nerve | Action | |
| sternohyoid | manubrium of sternum | hyoid bone | ansa cervicalis | depress hyoid bone | ||
| sternothyroid | manubrium | thyroid cartilage | Ansa cervicalis | Elevates larynx, may slightly depress hyoid bone | ||
| thyrohyoid | thyroid cartilage | hyoid bone | first cervical nerve | depress hyoid bone | ||
| omohyoid | Upper border of the scapula | Hyoid bone | Ansa cervicalis | Depresses the larynx and hyoid bone. Carries hyoid bone backward and to the side |
 |
| Anterior Superficial View |
| CERVICAL MUSCLES | FUNCTION | NERVE |
|---|---|---|
| Sternocleidomastoid | Extends & rotates head, flexes vertebral column | C2, C3 |
| Scalenus | Flexes & rotates neck | Lower cervical |
| Spinalis Cervicis | Extends & rotates head | Middle/lower cervical |
| Spinalis Capitus | Extends & rotates head | Middle/lower cervical |
| Semispinalis Cervicis | Extends & rotates vertebral column | Middle/lower cervical |
| Semispinalis Capitus | Rotates head & pulls backward | C1 – C5 |
| Splenius Cervicis | Extends vertebral column | Middle/lower cervical |
| Longus Colli Cervicis | Flexes cervical vertebrae | C2 – C7 |
| Longus Capitus | Flexes head | C1 – C3 |
| Rectus Capitus Anterior | Flexes head | C2, C3 |
| Rectus Capitus Lateralis | Bends head laterally | C2, C3 |
| Iliocostalis Cervicis | Extends cervical vertebrae | Middle/lower cervical |
| Longissimus Cervicis | Extends cervical vertebrae | Middle/lower cervical |
| Longissimus Capitus | Rotates head & pulls backward | Middle/lower cervical |
| Rectus Capitus Posterior Major | Extends & rotates head | Suboccipital |
| Rectus Capitus Posterior Minor | Extends head | Suboccipital |
| Obliquus Capitus Inferior | Rotates atlas | Suboccipital |
| Obliquus Capitus Superior | Extends & bends head laterally | Suboccipital |
| THORACIC MUSCLES | FUNCTION | NERVE |
|---|---|---|
| Longissimus Thoracis | Extension, lateral flexion of vertebral column, rib rotation | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Iliocostalis Thoracis | Extension, lateral flexion of vertebral column, rib rotation | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Spinalis Thoracis | Extends vertebral column | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Semispinalis Thoracis | Extends & rotates vertebral column | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Rotatores Thoracis | Extends & rotates vertebral column | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| LUMBAR MUSCLES | FUNCTION | NERVE |
|---|---|---|
| Psoas Major |
Flexes thigh at hip joint & vertebral column
| L2, L3, sometimes L1 or L4 |
| Intertransversarii Lateralis | Lateral flexion of vertebral column | Ventral primary division of spinal nerves |
| Quadratus Lumborum | Lateral flexion of vertebral column | T12, L1 |
| Interspinales | Extends vertebral column | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Intertransversarii Mediales | Lateral flexion of vertebral column | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Multifidus | Extends & rotates vertebral column | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Longissimus Lumborum | Extends & rotates vertebral column | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |
| Iliocostalis Lumborum | Extension, lateral flexion of vertebral column, rib rotation | Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves |

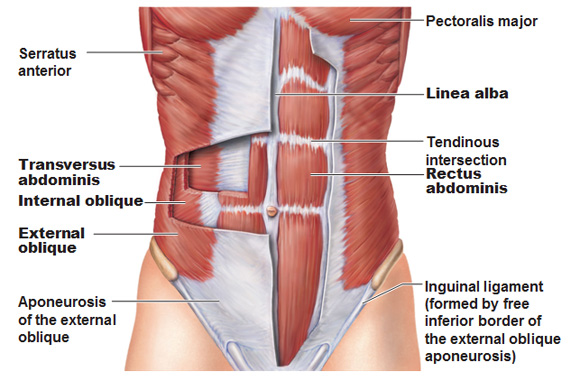
Muscles of the Abdominal Wall

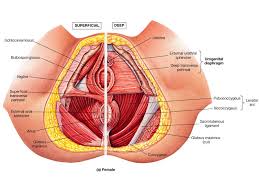
Muscles of the Pelvic Floor and Perineum
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coccygeus | ischial spine | side of the coccyx and lower sacrum | elevates the pelvic floor | branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 | ||
| iliococcygeus | arcus tendineus levator ani and the ischial spine | anococcygeal raphe and the coccyx | elevates the pelvic floor | branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 | ||
| levator ani | posterior surface of the body of the pubis, fascia of the obturator internus m. (arcus tendineus levator ani), ischial spine | anococcygeal raphe and coccyx | elevates the pelvic floor | branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 | ||
| obturator internus | the internal surface of the obturator membrane and margin of the obturator foramen | greater trochanter on its medial surface above the trochanteric fossa | laterally rotates and abducts the thigh | nerve to the obturator internus m. | ||
| piriformis | anterior surface of sacrum | upper border of greater trochanter of femur | laterally rotates and abducts thigh | ventral rami of S1-S2 | ||
| pubococcygeus | posterior aspect of the superior pubic ramis | coccyx | elevates the pelvic floor | branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 | ||
| puborectalis | posterior aspect of the body of the pubis | unites with the puborectalis m. of other side posterior to the rectum | draws the distal rectum forward and superiorly; aids in voluntary retention of feces | branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 | ||
| pubovaginalis | posterior aspect of the body of the pubis | fascia of the vagina and perineal body | draws the vagina forward and superiorly | branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 |
Muscles of the Forearm and Hand Movements


Muscles for Leg Movements
| Thigh | Origin | Insertion | Action | Notes |
| Posterior thigh | See also: Stretches | |||
| (Hamstrings) | Hamstring Stretches | |||
| Biceps Femoris | Long head -Ischial tuberosityShort head- lateral lip of linea aspera | Head of the fibula | Flex knee, extend hip, tilt pelvis posteriorly, laterally rotates femur | |
| Semitendinosus | Ischial tuberosity | Proximal, medial condyle of the tibia | Flex knee, extend hip, tilt pelvis posteriorly, medially rotate of flexed knee | superficial, stringy, tendonus attachment |
| Semimembranosus | Ischial tuberosity | Posterior medial condyle of the tibia | Flex knee, extend hip, tilt pelvis posteriorly, medially rotate flexed knee | deeper, broader, most medial |
| Anterior Thigh | ||||
| Sartorius | Anterior superior iliac spine | Upper medial shaft of tibia | assists flexion, abduction, lateral rotation of hip, assists flexion, medial rotation of knee | cross-legged flexion: the tailors muscle |
| Quadriceps | ||||
| Rectus femoris | anterior inferior iliac spine, ilium on upper margin of acetabulum | patella, patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity | extension of knee, assists flexion of hip | only hip flexor of quad group |
| Vastus medialis | linea aspera on posterior femur | patella, patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity | extension of knee | |
| Vastus lateralis | linea aspera on posterior femur | patella, patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity | extension of knee | |
| Vastus intermedius | anterior and lateral femoral shaft | patella, patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity | extension of knee | |
| Medial thigh | Groin Stretches | |||
| Pectineus | superior ramus of pubis | pectineal line of femur | flexes hip, adducts thigh, medially rotates the thigh | |
| Adductor longus | anterior pubis just inferior to pubic tubercle | linea aspera on posterior femur | adduction of hip, assists in flexion and medial rotation of hip | |
| Adductor brevis | anterior pubis | linea aspera on posterior femur | adduction of the hip, assists in flexion and medial rotation of hip | |
| Adductor magnus | inferior pubic ramus, ischial ramus, ischial tuberosity | proximal 1/3 of linea aspera of posterior femur, adductor tubercle | adduction of hip, assists in flexion of hip, posterior fiber assists in extension of hip | assist hamstrings |
| Gracilis | anterior pubis | medial proximal tibia | adduction of hip, assists in flexion and medial rotation of flexed knee | crosses knee and hip |
| Leg, ankle, foot, posterior thigh | ||||
| Gastrocnemius | medial epicondyle of femur, lateral epicondyle of femur | calcaneus via achilles tendon | plantarflexion of foot at ankle, flexion of knee | crosses knee and ankle |
| Soleus | upper fibula, soleal line of tibia | calcaneus via achilles tendon | plantarflexes foot | deep to gastrocnemius, but wider than gastroc; strong contractions pump blood from leg to heart |
| Plantaris | above the lateral head of gastrocnemius on femur | calcaneus via achilles tendon | weak plantarflexion of the foot at ankle | may be absent in approx. 10% of people |
| Popliteus | lateral femoral condyle | posterior tibial surface above soleal line | laterally rotates femur, flexes the knee, unlocks knee from and extended position | deepest muscle of posterior knee |
| Tibialis posterior | proximal posterior tibia, interosseous membrane, medial fibula | navicular, cuneiform, cuboid bones and bases of 2nd -4th metatarsals | inverts the foot, plantar flexes the ankle | tendons under flexor retinaculum |
| Flexor digitorum longus | lower 2/3 of tibia | 4 outer phalanges plantar surface, along side ankle | plantarflexes and inverts foot, flexes toes 2-5 | |
| Flexor hallicus longus | inferior 2/3 of posterior fibula | plantar surface of big toe | flexes big toe, weak plantarflexion of the ankle, inversion of foot | |
| Anterior leg | Stretches for shin splints | |||
| Tibialis anterior | lateral tibia, proximal lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane | medial cuneiform, first metatarsal | inversion of foot, dorsiflexion of ankle | |
| Extensor digitorum longus | lateral tibial condyle, fibula | dorsal surface of phalanges 2-5 | extension of toes 2-5, dorsiflexion of the ankle, eversion of the foot | |
| Extensor hallicus longus | medial aspect of the fibula, interosseous membrane | diatal phalanx of big toe | extends the big toe, dorsiflexion of the ankle, inversion of the foot | |
| Lateral leg | ||||
| Peroneus longus | upper lateral fibula | medial cuneiform, plantar surface of cuboid, base of 1st metatarsal | eversion and abduction of foot, weak plantarflexion of foot | |
| Peroneus brevis | lower, lateral 2/3 of fibula | fifth metatarsal | eversion and abduction of foot, weak plantarflexion of foot |




Walang komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento